|
 |
|
|
Supercapacitors |
|
|
Supercapacitors, which are also known as electrochemicalcapacitors or ultracapacitors, have attracted considerable interest as a unique class of energy storage devices with high power capability, long cyclic life, low maintenance requirements, and rapid dynamics of charge propagation. We have been developing a range of electrode materials for high performance supercapacitors based on graphene, metal oxides, and conducting polymers.
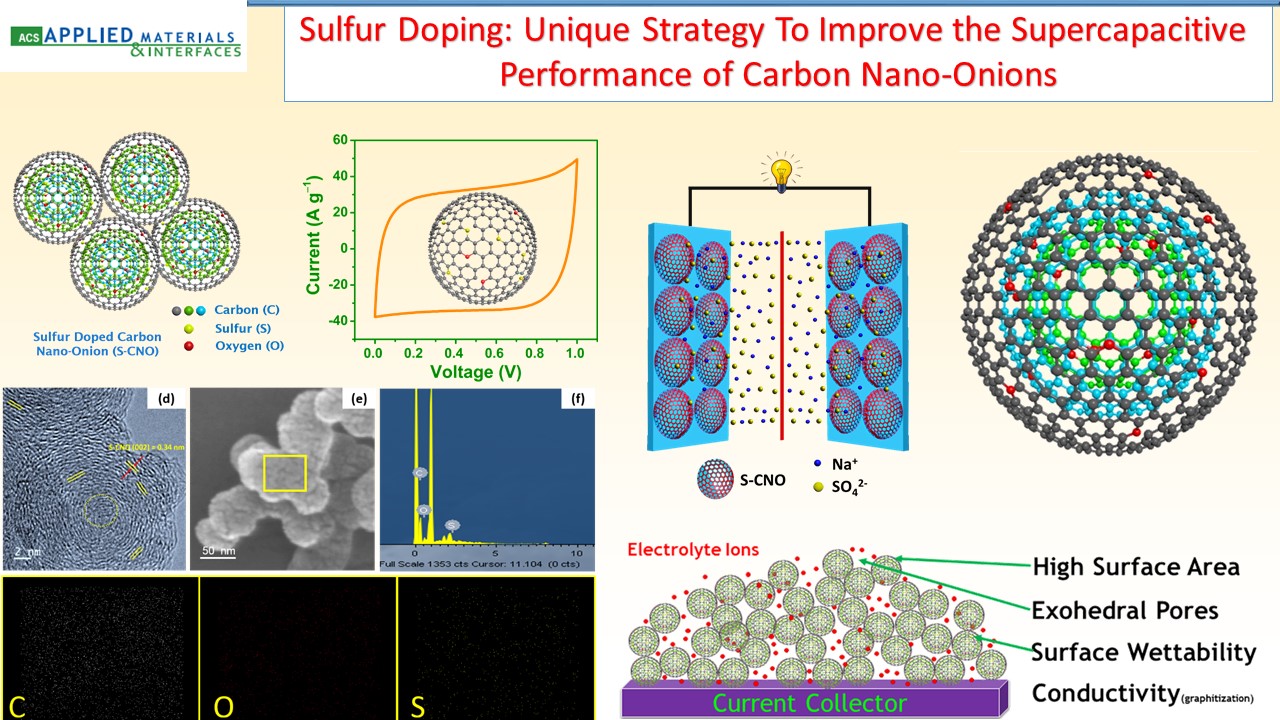
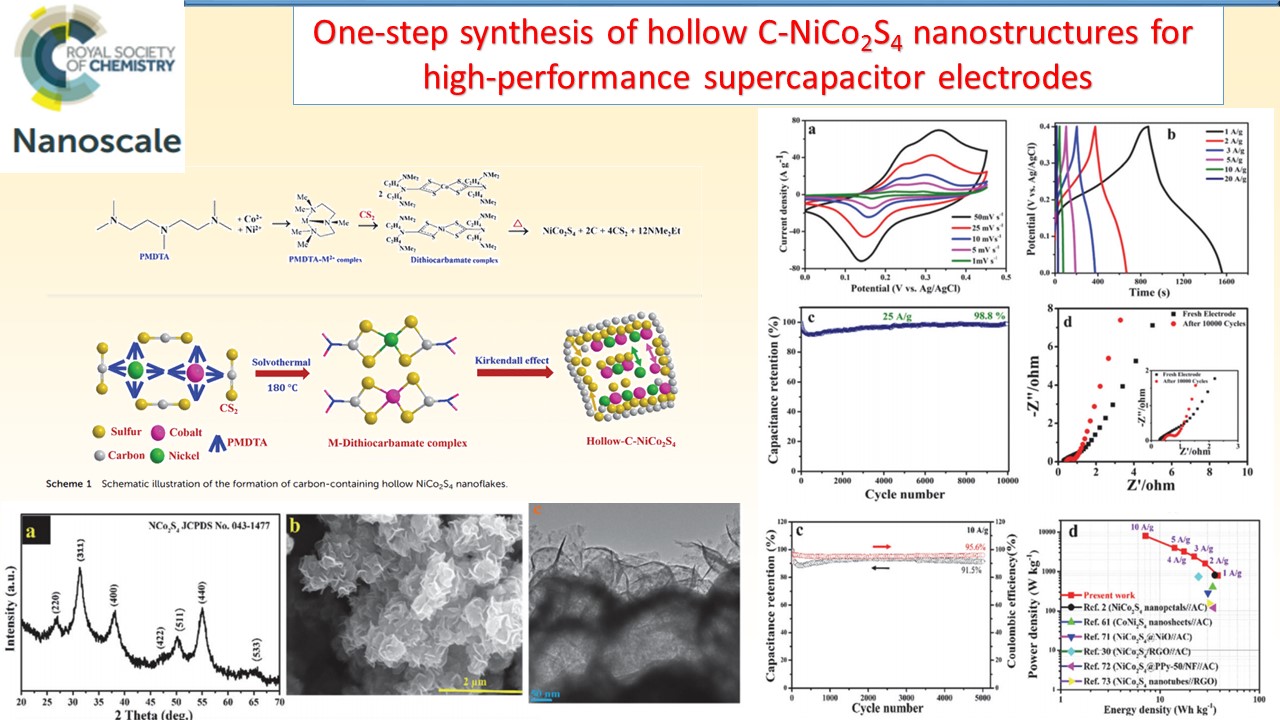 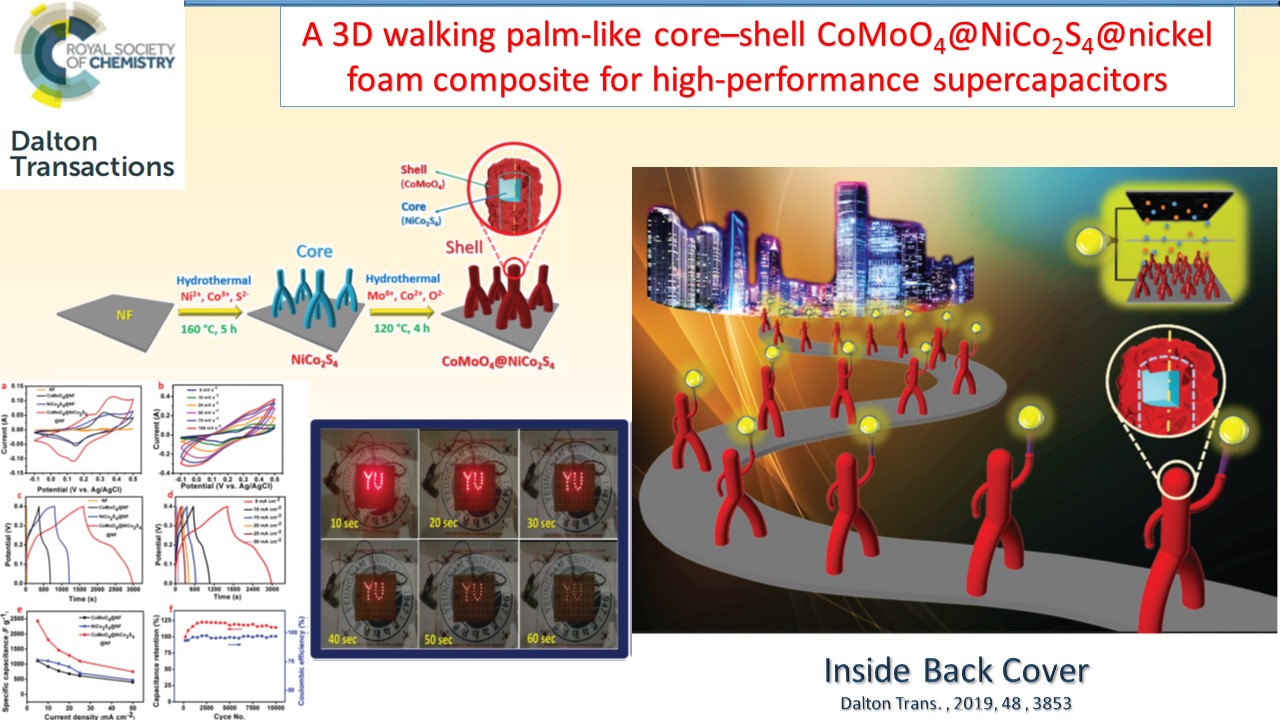
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| |
Electrochemical Sensors |
|
|
Electrochemical sensors device can provide specific quantitative/semiquantitative information about the analyte molecules through the transducer. In our research group, successfully developed various types of electrode materials like electrochemically reduced graphene oxide composite, and redox active polymer/metal oxide/sulfide modified electrodes for chemical, environmental pollutant and bioactive molecule sensor.
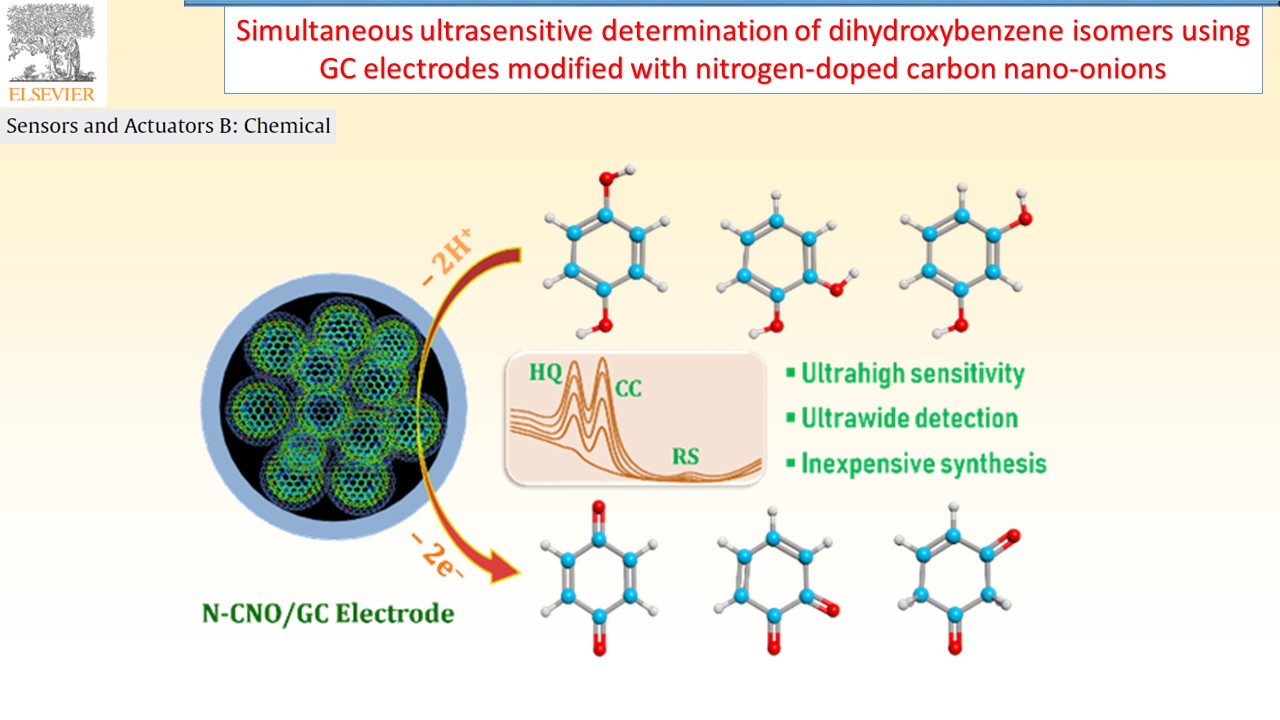
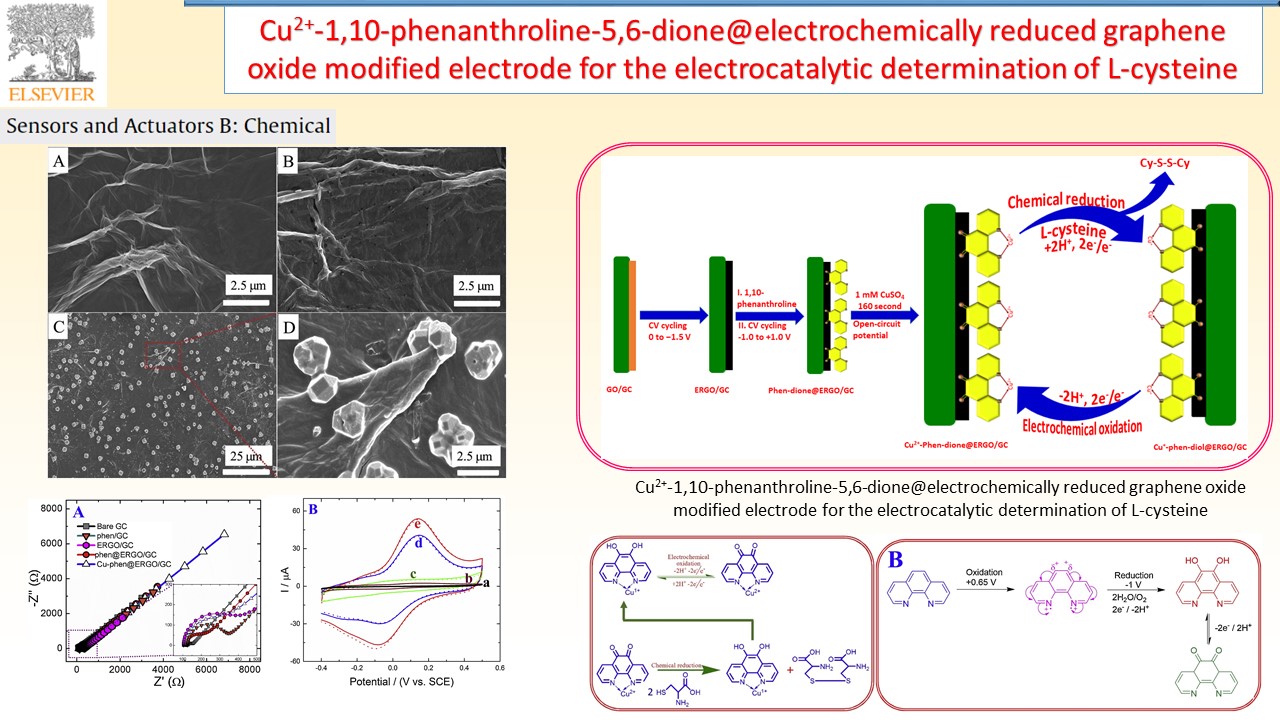
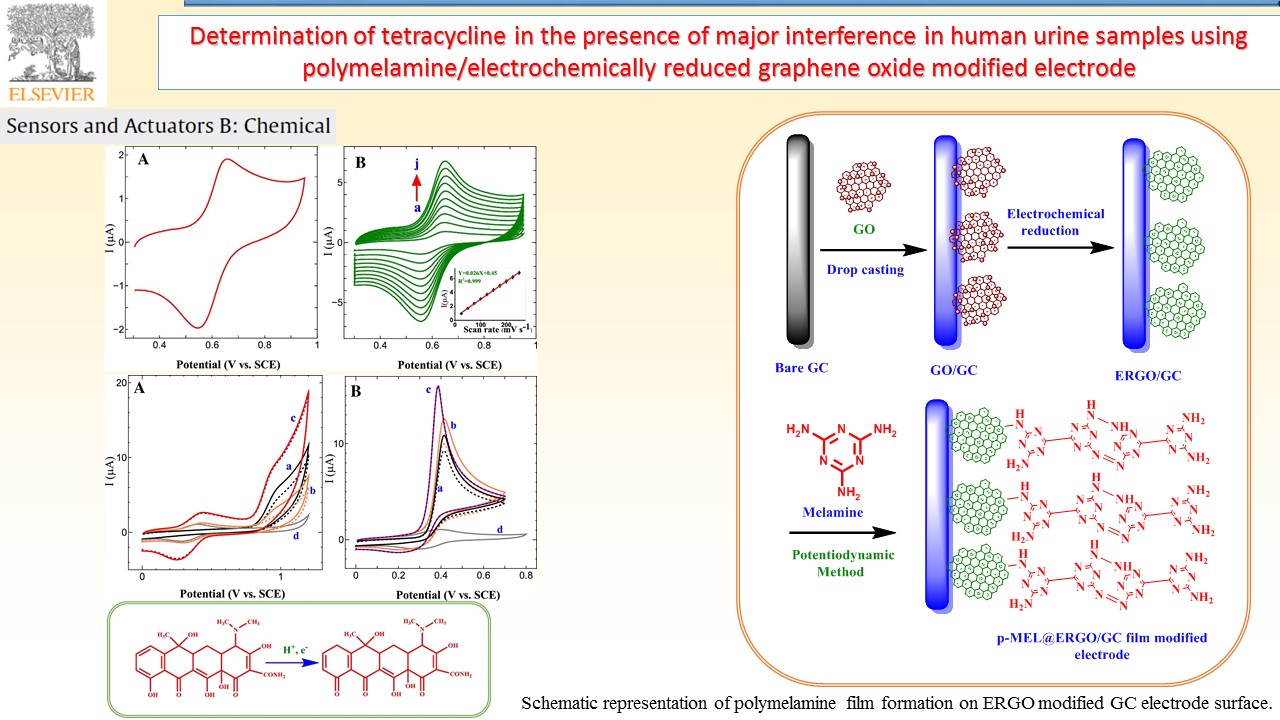
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Nanocomposites |
|
|
Since 2008, we have been working on the synthesis of nanocomposites using solvents including water, ionic liquids, and supercritical carbon dioxide. These nanocomposites consist of carbon nanotubes, graphene, metal/metal oxides, nanoparticles, and polymers. The as-prepared products were investigated for different applications, such as sensors, antibacterial materials, and photocatalysts.
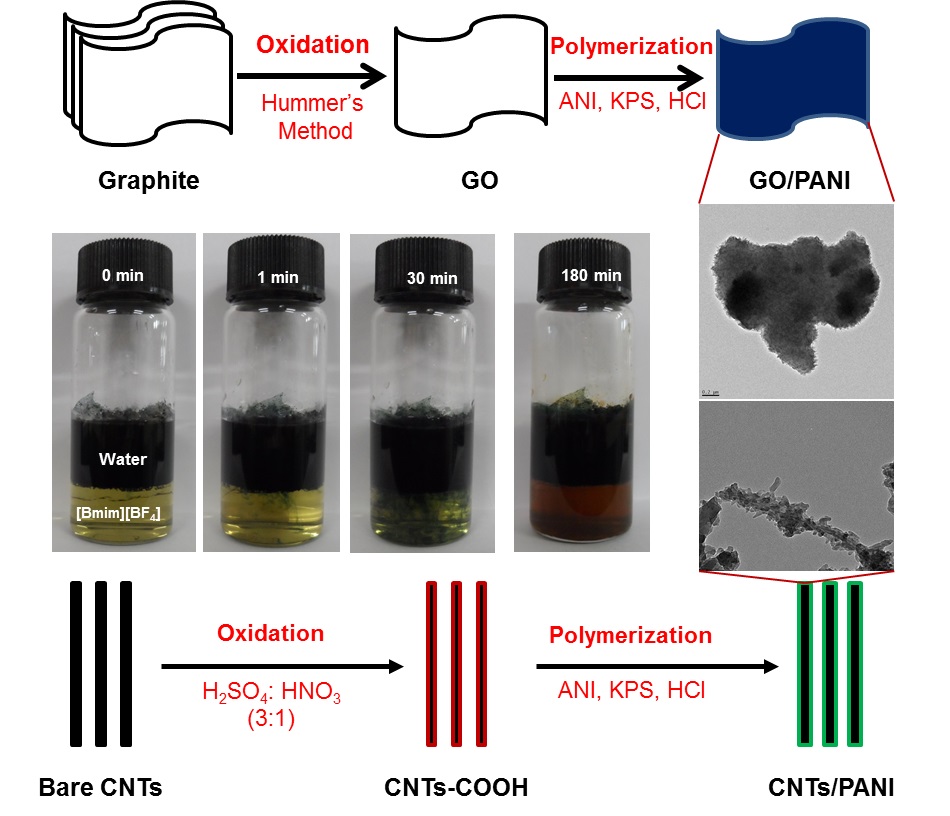

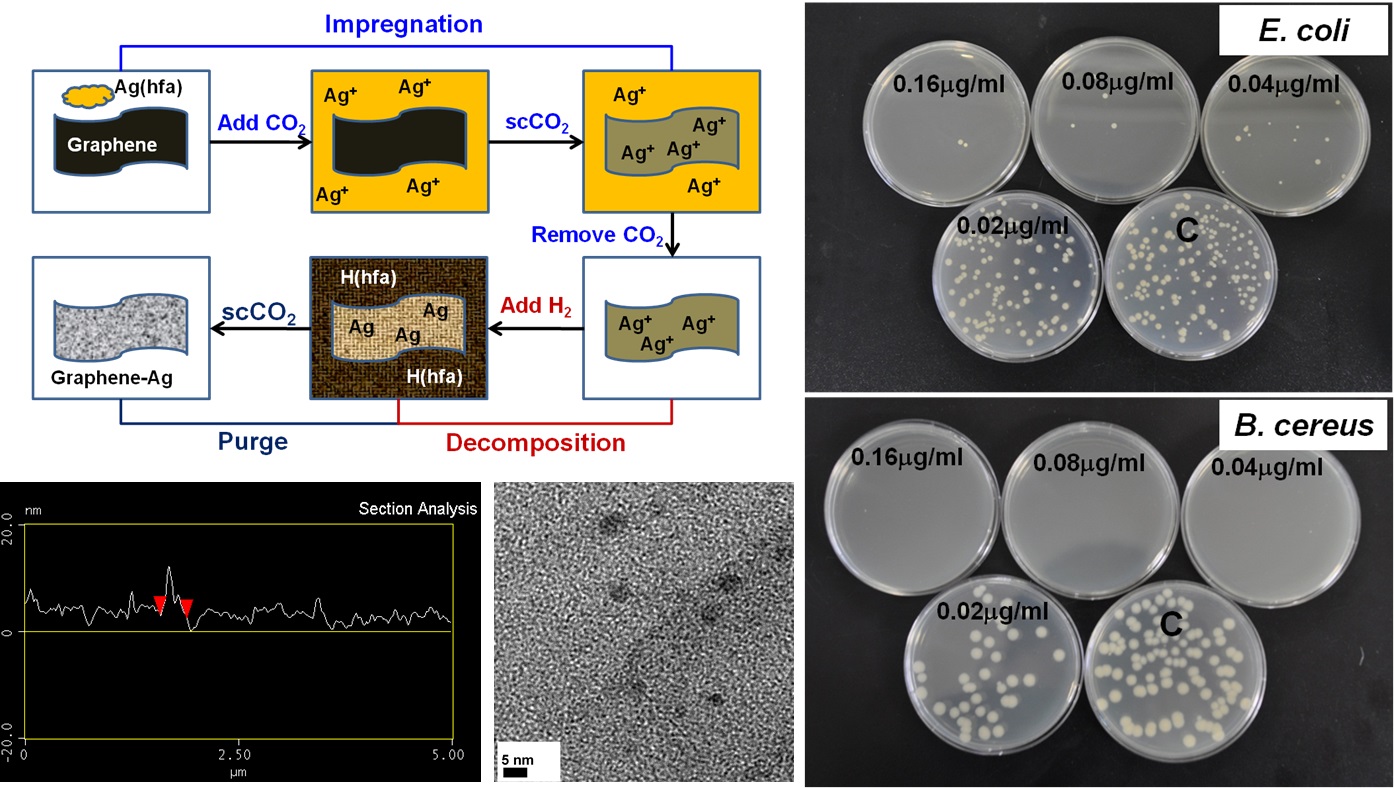
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
Ionic Liquids |
|
|
We have been working on the synthesis of polymers and nanocomposites using ionic liquids as solvents. Ionic liquids are considered environmentally friendly solvents, as they are nonvolatile, nonflammable, and recyclable . They also have good solubility in many organic and inorganic compounds. Radical polymerization in ionic liquids results in higher polymerization rates and higher molecular weights than in bulk or organic solvents.
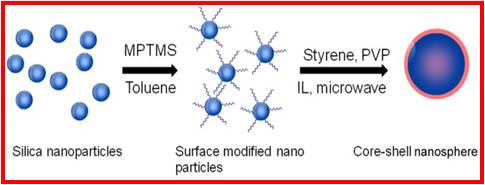

|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
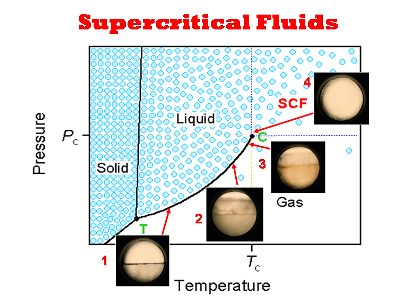
Supercritical Fluids |
|
|
Supercritical fluid technology has focused on many applications such as foods, pharmaceuticals, polymers, semiconductors, bio-materials, reactions, and environmental treatments. Supercritical fluids have unique characteristics of tunable solubility with a small change in temperature or pressure. Supercritical carbon dioxide is widely used because it has mild critical conditions, and is nontoxic, nonflammable, environmentally-friendly, and inexpensive. It does not leave any residue after treatment, and can be easily separated and recycled, and is chemically inert. We have been developing pollution-free processes for synthesizing polymers using supercritical carbon dioxide to improve polymer properties.
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| |
Clean Technology |
|
|
We have been working on the project “Clean reaction process using supercritical fluid” as a Basic Research Project of Korean Science and Engineering Foundation, including high molecule synthesis in supercritical fluid (PMMA/PEHA - raw materials for paint and adhesives, PLA-decomposable high molecule), chemical reaction (radical and wittig reactions), and decomposition of PET with supercritical methanol into monomers of dimethyl terephthalate and ethylene glycol.

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|



